Version 10
Complex numbers and turtle module
March 13, 2019
Exact calculation with complex numbers
The results of calculations involving complex numbers are now given in exact and approximate form.
The quotients of complex numbers are simplified.

The arguments of complex numbers are computed in a form involving the number pi.

In the Settings application it is possible to choose the format of numbers in the Complex format section.
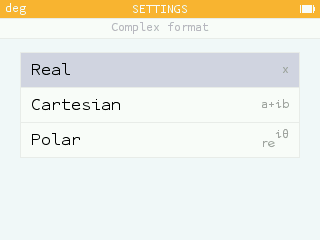
The Real option, set by default, gives the roots of polynomials in R, for example. With this option, sqrt(-1) returns the result: unreal.

You can also activate the Cartesian and Exponential options which give complex results in cartesian or exponential form. In this case, the roots of the polynomials are given in C and sqrt(-1) returns i or exp(i*pi/2) depending on the setting.

Turtle module in Python
It is now possible to use the turtle module for Python. This provides access to a simple and ideal drawing tool for teaching algorithms.
The functions available in the turtle module are listed in the Modules section of the Toolbox menu as well as in the Catalog.
A sample script squares.py has been added to the home screen. To draw the figure, run the command squares().
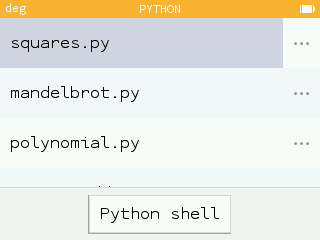
- The turtle drawing can be interrupted by pressing the Return key.
Improved graphing interface
Grid colors now indicate major and minor tick marks.
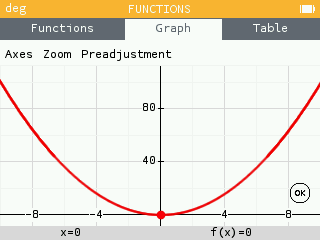
When the zoom does not show the axes, it is now possible to see the values of the tick marks.
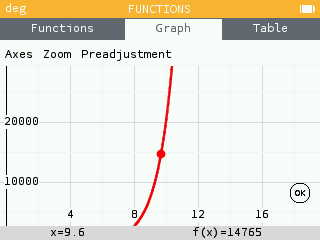
When overlaying the grid values, only the extreme values are displayed.
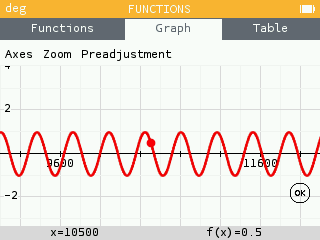
- The automatic adjustment of certain functions such as
sin^2+cos^2has been adapted. - The legend of the graph takes into account the scope of the function. For example,
f(x)=x/xreturns the valueundefat0. - When the user deactivates the Y auto option and adds a function, the chosen axis scale is kept.
And also...
In natural edit mode, when the user presses the division key after writing a multiplication, the fraction line runs the length of the multiplication.
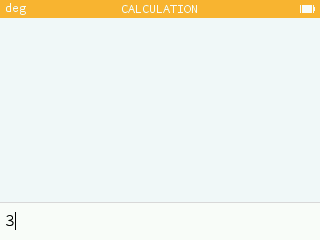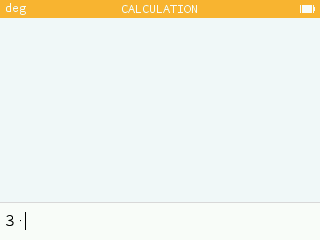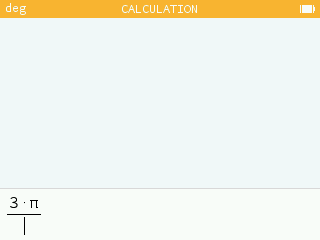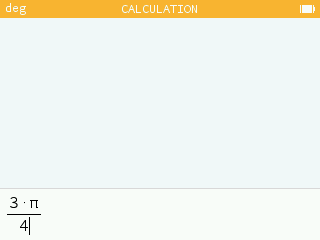
In the Calculations, application, when the result is a polynomial involving a symbol, the powers are listed in descending order.

In the Calculations and Sequences applications, a = symbol has been added next to f(x) and Un.
- The maximum mu / sigma limit has been increased in the Probabilities applicaiton.
- Correction of rounding errors.
Special thanks
We would like to thank Jean-Baptiste Boric who greatly helped in the development of this update. We also thank Rémy Da Costa Faro and Roman Wueest for their contributions.